SEO, or search engine optimization, is the process of organically improving your ranking on a search engine result’s page. It involves optimizing your website so that search engines display your web pages as top results for relevant search queries. Let’s take a look at the basics of SEO, its types, and why SEO matters.
Content
- How do search engines work?
- The basics of search engine optimization
- Conclusion: Why SEO matters and how long is the optimization process?
How do search engines work?
Search engines perform three primary functions:
- Crawling: Involves using search engine spiders or web crawlers to go over the entire web for content. It’s similar to how a spider crawls its web in search of trapped insects or food bits. Search engine spiders are scripts or robots that find new, updated, and missing content.
- Indexing: Involves storing and organizing all content found as a result of crawling the web. Once your web page is indexed, it can be displayed on Search Engines Results Page (SERPs) to answer a user’s query. Every search engine processes and stores an index—a database of web pages that can appear on search results.
- Ranking: Search engines rank websites to provide the best results for a searcher’s query. This means that SERP lists websites in order of relevance to a query. When you search Google for electric cars, Google goes through its index for web pages that target the keyword electric cars.
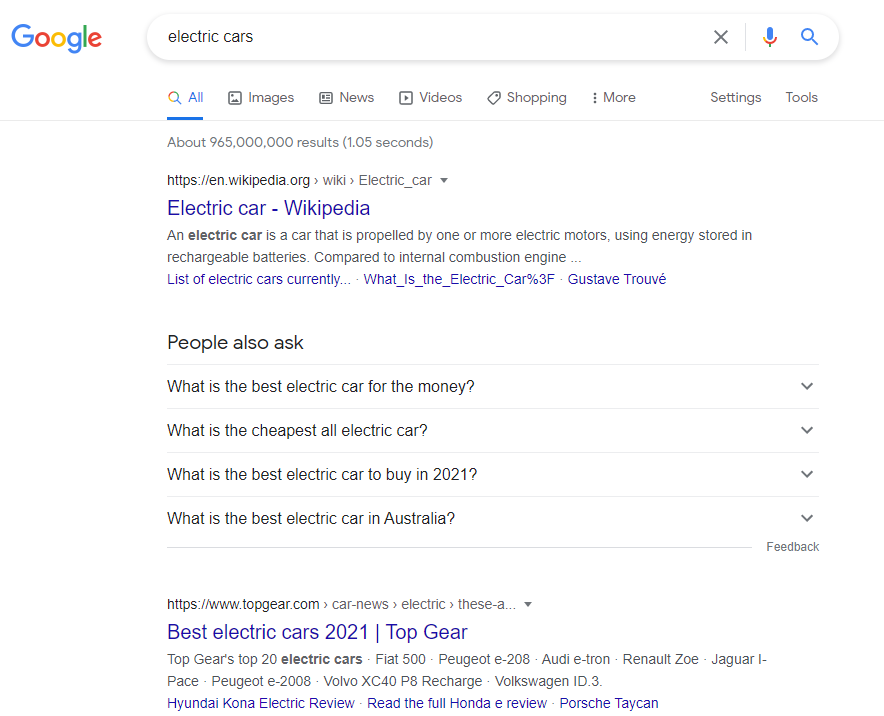
Then it arranges these web pages in order of relevance, hoping that the first results provide everything you need to know about electric cars. There’s a running joke about Google’s ranking algorithm’s excellence. The best place to hide a dead body is page 2 of Google search results. This joke implies that most users find answers to their queries on Google’s first SERP.
The basics of search engine optimization
A good SEO strategy starts with proper keyword research. Then, you start creating valuable content that meets a user’s search intent by providing answers to their queries. But search engine optimization goes further and deeper.
Let’s start with the most important SEO Basic every beginner must know.
1. Keyword research
Keyword research involves finding search phrases that are relevant to your web content. By our definition, keywords are words and phrases that are commonly used in search queries. First, you must understand your target audience and how they search for products or services related to yours.
• Discover what people are searching for
What does your target audience ask Google? What search keywords do your competitors rank for? How many people are searching for it? How do they want answers—in pictures, videos, or text content? Answering these questions is the first step in keyword research.
• Use a keyword tool
If you’ve created a shortlist of search phrases your target audience is using, you can further your research using keyword tools. Keyword tools are websites and programs that help you discover both long-tail and short-tail keywords to target. These tools also help you see who is searching for your keywords and how often people search per month.
• Understand long-tail keywords
Long-tail keywords are search phrases that often contain up to four words. Using long-tail keywords helps you target searchers whose search intent matches your web page’s content. Long-tail keywords with low search volume frequently convert better because searchers are more specific and intentional in their queries.
For example, the long tail keyword “best mountain bikes under $100” has a low search volume and keyword difficulty. Someone searching for mountain bikes is probably just browsing. But someone searching for “best mountain bikes under $100” wants to buy one.
• Discover search intent behind keywords
There are four major categories of search intent:
1. Informational intent: The user wants information such as a celebrity’s age or the number of countries in Asia.
2. Navigational intent: The user wants to go to a particular webpage, such as Adsterra’s homepage or an ESPN blog post.
3. Transactional queries: The user wants to buy something or use a service, such as tickets to a music concert or spare car tires.
4. Commercial intent: When there’s a likelihood that a user can become a business lead or a customer. You can evaluate commercial intent by looking at the number of people that advertise on a specific keyword in Google Adwords.
Use these categories to understand how to use keywords in your content. A person searching for how tall the Statue of Liberty is doesn’t want to go there themselves. So web pages offering tours to the Statue of Liberty are irrelevant.
2. On-site optimization
On-page SEO, or On-site SEO, is the practice of optimizing your web pages to satisfy search intent and rank higher in search results pages. On-page SEO involves:
- Creating high-quality, valuable, and unique content.
- Optimizing your title, headings, and subheadings by including long-tail keywords.
- Putting your page’s titles and subheadings in header tags.
- Using a diverse cluster of keywords and getting the recommended keyword density (1- 2%).
- Optimizing images by adding alt texts and compressing their sizes.
- Using anchor texts to add internal and external links that point visitors to more detailed and valuable content.
- Using short and readable URLs.
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO is the practice of ensuring that your website meets the technical standards of current search engines with the intent to improve organic rankings. Crawling, indexing, rendering, and website architecture are all important aspects of technical SEO.
Why Is Technical SEO Necessary?
You can have the best website in terms of content quality and design. But if your technical SEO is poor, you’ll not move up in Google’s SERPs.
At a bare minimum, search engines must be able to locate, crawl, render, and index all web pages on your website. Also, a fully technically optimized webpage must be safe, mobile-friendly, devoid of duplicate content, must load very fast, and more.
Your technical SEO doesn’t have to be perfect to rank. But, the easier you make it for Google to access your content, the greater your chances of ranking. Technical SEO involves optimizing your 301 redirects, Structured Data, Hreflang, URL structure, Canonical tags, Site architecture, e.t.c.
4. Link building
What is the purpose of link building? Link building is perhaps the most vital component of any successful SEO strategy. It entails obtaining backlinks from other websites to yours—a simple dofollow hyperlink from one website to another.
Most SEO experts agree that link building is the most challenging aspect of search engine optimization and the most beneficial. Consider backlinks from other websites as votes. The more backlinks from higher-quality domains pointing to your website (and therefore being part of your backlink profile), the higher you’ll rank on search engine results pages.
So, how can you receive free high-quality backlinks from highly authoritative websites?
- Publish Superior Content That Outperforms Competitors
The first step in surpassing the top-ranked sites is to study what is already ranking and improve it. For example, comprehensive guides rank quite high in search engines since they are lengthy and contain several resources.
If your website doesn’t contain a lot of texts — File Converters, URL Shorteners, File Hostings — You should ensure that it is very user-friendly.
- Link to High Authority Websites and Inform Them
External links in your website determine how search engines rate your content’s quality. Google wants to determine the trustworthiness of your website, so it analyzes the backlinks you provided to your readers to aid in its ranking process.
Another simple approach to getting backlinks is informing these websites about your backlinks to their domain. There’s a chance that they will link back to you.
- Contribute Guest Articles
Guest posting involves writing articles for other websites and placing a backlink to your website in the article’s content. Your guest post pitch must be detailed and very relevant to your niche and the other website’s niche.
Your guest article must be comprehensive, incredibly informative, and publishable. Suppose your content is thin (but publishable) and providing little value to the reader. In that case, it’ll not generate interest and traffic back to your website, harming your chances of guest posting in the future.
5. Measuring & tracking SEO success
Measuring your SEO’s impact is vital to your success and growth. It’ll go a long way in helping you rethink your approach when something isn’t working.
Monitoring everything from rankings and conversions to lost backlinks and core web vitals helps determine the power of your SEO. So what should you track and measure?
- Conversion Rates
Conversion rate is the number of conversions (for a single intended action/goal) divided by the total number of unique visits. A conversion rate applies to any action: email signup, purchase, or account creation. Knowing your CTR (click-through-rate) and conversion rate helps you estimate the potential return on investment (ROI) from your website traffic.
- Average Session Duration
How much time do users spend on your website? Session Duration refers to the time during which a user engages in regular active interactions with a website. When the user is inactive for a predefined time, the session is timed out (30 minutes by default). Session duration takes into account the total amount of time spent on a website by a user.
- Bounce Rate
Bounce refers to a single-page session on your site. In Analytics, a bounce is defined as a session that generates just one request to the Analytics server. For example, when a user visits a single page on your site and then quits the session without causing any additional queries to the Analytics server.
Is it bad to have a high bounce rate? Yes, a high bounce rate is negative if your website’s success depends on users viewing more than one web page.
- Scroll Depth:
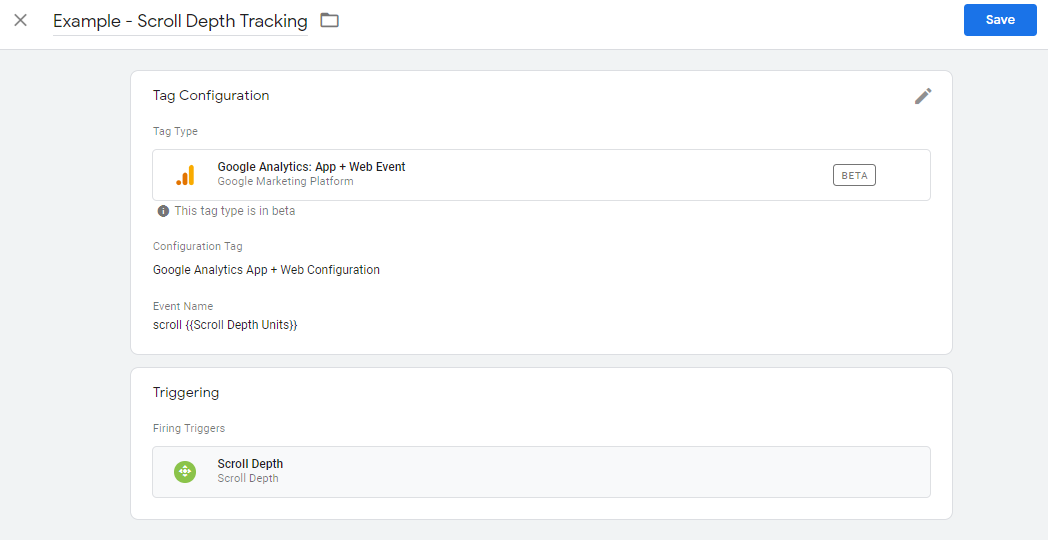
Scroll depth measures how far users scroll down a specific webpage. It helps you determine if users are reaching the most critical part of your content. You can track this metric by setting up a trigger on Google Analytics. If your page’s objective is a form fill, you can specify that as a goal. You’ll be able to observe when site visitors convert your reports.
- Organic Traffic:
While ranking is an important SEO statistic, evaluating your site’s organic performance cannot end there. The goal of ranking is to attract organic traffic by appearing top of the search results for a user’s query.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR refers to the percentage of users that clicked on your webpage from search results. This metric provides insight into how well your web page title and meta description are optimized.
White hat vs. Black hat
Black hat SEO focuses on optimizing your content for the search engines only, not considering humans who interact with your content. It involves bending and breaking several rules to make a website rank higher than it should. For example, Rich Snippet Markup Spam, Article Spinning, and Keyword Stuffing.
On the other hand, White hat SEO involves optimizing your website in compliance with search engines’ best practices and rules. It’s the best way to build your website’s rank organically. White hat SEO is human-centric, i.e., content is created and optimized to improve user experience and completely satisfy search intent.
Like life, SEO’s not always black or white. Gray hat SEO involves practicing both white and black hat SEO tactics. With this approach, you’re trying to get a distinct advantage by following loopholes in some SEO rules. For example, Google frowns at guest posting to build backlinks and domain authority. However, guest posting is an honest attempt to build brand awareness and create business leads by directing organic traffic to your website.
Gray hat SEO is not as pure as white hats and not as bad as black hat practices.
Conclusion: Why SEO matters and how long is the optimization process?
Here’s an interesting fact: In 1997, there were approximately 1 million websites. This figure doubled to 2.4 million in 1998. By 2010, there were 200 million websites online. Today there are over 1.5 billion websites on the internet.
Why should this matter to you?
When someone uses Google or Bing to search for information, they have access to a billion websites (and exponentially more web pages).
The internet is like our expanding universe, and SEO is critical because your website will be relegated to its fringes without it. Google and other search engines may index your website, but does it really exist if your target audience never sees it on the SERPs?
Search engine optimization (SEO) ensures that your target audience finds your website when conducting a relevant search. For example, if a user wants to read about SEO for beginners, we’d like the top results on any search engine to show them this article.
SEO is still the primary step to generating a significant traffic flow. The more users visit your website, the more ad impressions you can deliver and the higher your revenue becomes. It is never too late to start optimizing a website, just as it is never too late to start getting passive income from advertising.
