Every publisher dreams of driving the highest traffic possible to their website. After all, traffic translates into revenue, and that’s the end goal. Some webmasters resort to bots to automate fake traffic to their sites, making it look like they have more viewers than they do. Long term, this is a terrible approach.
Bot traffic comes from automated software designed to perform repetitive, simple tasks within a short period. On the receiving end, we consider it spam and don’t want it near our reports. Why? Because it distorts our KPIs and gives us false impressions of website growth. Today we will explain why fake or bot traffic is nothing but a disaster and tackle it.
What is bot traffic?
Bot traffic refers to the presence of non-human visitors on your website. Whether you have a large, well-known website or a new one, a specific portion of bots will visit you at some point.
Some bots carry out repetitive tasks such as copying, ad clicking, commenting, or other malvertising activity.
While some publishers buy fake traffic on purpose, others are defrauded. These companies typically buy traffic from third-party providers who automate the process to inflate the value of the site, blog, or social media channel to monetize it better or sell it for a higher price. However, artificially generated traffic to a website is not as valuable as real people.
Why bot traffic is bad for your website
Here are some of the reasons you should never engage in buying bot traffic and why you should remove any false numbers on your analytics:
Instability of traffic
Bot traffic is not stable and does not match your overall traffic behavior. Imagine a rapid rise in metrics followed by a rapid decline.
Rather, legitimate traction provides predictable stability. Stable traffic means humans trust and uses your site.
No conversions
Your website’s goal should be more than just traffic. Only a tiny percentage of your viewers should be persuaded to convert or take the necessary actions to justify your ad campaign.
Fake traffic can’t be monetized and doesn’t help your conversion rate.
Risk of sanctions and penalties
Ad networks may penalize you if you receive bot traffic on your website. These networks are tasked with protecting their advertisers from fraudulent activities, i.e., they can terminate your account quickly. You may also face Google penalties and demotions on search platforms, among other consequences.
Bad for SEO
Another critical area where fake traffic affects your website’s health is SEO. Fake clicks make it difficult for you to analyze your site’s search engine performance.
Poor web performance
Fake clicks will inevitably impact your website’s performance, including load time and DDOS vulnerability.
Loss of integrity
Bots can damage your reputation with real customers, clients, or partners. Advertisers can easily detect fake viewers and will terminate contracts or blacklist you as a traffic source.
Good vs. bad bots
To properly understand bot traffic, you need to consider the various types of bot traffic, including web crawlers for search engines and malicious bots that attack websites.
Good bots perform operational tasks such as old data scraping, content hygiene, and data capturing. They help users to have a productive internet browsing experience. Bots such as search engine crawlers, feed fetcher bots are helpful.
Bad bots engage in all fraudulent and malicious activities resulting in losses for both publishers and advertisers.
Examples of good bots:
- Search Engine Bots: Search engine bots are the first and most prominent type of good bot traffic. These internet bots crawl the entire web and assist website owners in listing their sites on search engines like Google, Yahoo, and Yandex. Although bot traffic requests may be automatic, they are good bots.
- Partner/Vendor bots: Third-party service providers send these bots. When you use SEO tools such as Ahrefs or SEMRush, their bots crawl your site to access your SEO performance. Partner bots like search engine bots provide helpful services by optimizing the website’s performance for human visitors and limiting the number of requests.
- Copyright bots: Ensuring that no one takes your photos and personalizes them can be difficult. With so many websites to check, an automated bot is the only solution. These web bots crawl the internet looking for specific images to ensure that no one uses copyrighted content without permission.
Bad bots
Bad (malicious) bots, unlike good bots, ignore your robots.txt rules. They also hide their identity and source, and they frequently appear like real human users. However, the main difference between bad bots and good bots is the type of tasks they perform. Bad bots perform disruptive and destructive tasks such as sending fake or spam traffic and ad fraud.
Common examples of bad bots:
- Spam: These spambots leave phishing messages or total crap in your blog’s comment section.
- DDoS: Hackers often use these bots to bring down your website using a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack.
- Ad Fraud: Bots click on your ads automatically and boost ad click payouts.
- Malicious attacks and ransomware: Bots can cause all sorts of havoc, including ransomware attacks, which encrypt devices and demand a payment to ‘unlock’ them.
How to identify bot traffic?
Malicious bots are becoming more intelligent. According to Imperva’s Bad Bot Report, Bots drive nearly 40% of internet traffic in 2022, with bad bots responsible for most of that traffic.
Every hour, bot traffic hits websites. Many publishers don’t understand why and how bot traffic affects their efforts and how to deal with it. So, we’ll begin with the first question: how can publishers identify if their traffic comes from bots?
Check your page load speed
A significant decrease in page speed, especially when there are no changes in your website, is a sure sign of bad bot traffic. It’s possible that a cluster of bots is attempting to overload your servers and shut them down. You’ll need to examine your KPIs (Key performance indicators) closely.
Trace the sources and find the one with soaring traffic
A website’s traffic comes from many sources. Sometimes the spike in traction comes from a single source. When this happens, a malicious bot may be attacking your site.
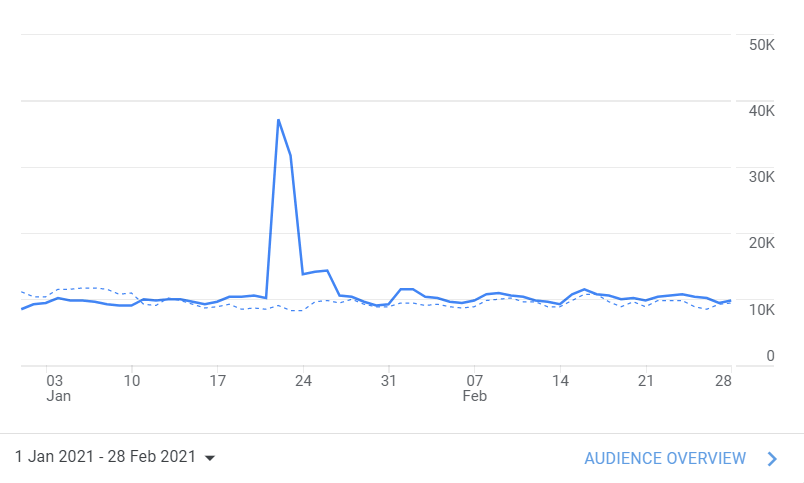
Real traffic comes via many channels, including search engines, referral links, and paid traffic.
Keep a tab on specific metrics
If you notice a sudden increase in traffic and bounce rate simultaneously, your website traffic is likely a bot. High traffic means a high frequency of the same bots is visiting your site repeatedly.
A high bounce rate means non-human traffic enters your site for no reason and leaves without visiting any other pages. A sharp drop in session duration also indicates bot traffic.
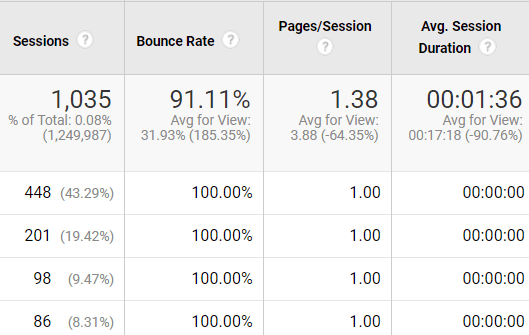
Assume your site primarily serves lengthy content having an average session of two to five minutes. Bot traffic reduces the average session duration.
Verify traffic sources and IP address
Besides the above metrics, some data sources serve as traffic emergency signals. A frequent and high number of visits from the same IP addresses indicates that you’re getting bot traffic.
Also, traffic from unknown sources may indicate bad bot traffic. For example, if most of your traffic comes from a particular country and there’s a sudden increase in traffic from a different country: this is an indicator of bot traffic.
If you’re a newbie, it’s best to start with your Google Analytics to understand traffic identification completely.
Try checking browser versions or devices
The above suspicious geolocations, multiple visits, and outdated browser (and device) versions should raise suspicions. If you see 2589 visits from Nokia N8, be concerned.
These attacks target popular browsers and devices. It also means you should look for unusual traffic spikes from a particular browser or device.
Mike Sullivan, a Google Analytics expert and top contributor, shares how his team detected fraud traffic by the Browser Size dimension.
Test for duplicate content
Your content is the primary purpose of your website, and when the bot attacks, it loses its meaning. Check for duplicate content to ensure that no scraper bots are present on your site.
Tools such as SiteLiner, Duplichecker, and CopyScape are essential in checking if your content appears elsewhere or changes in your content purpose.
Filter referral traffic sources
As you may have guessed, statistics tools are your primary means of detecting fake traffic. Which other filters can you apply? Try filtering your traffic by source or medium. Websites that refer to you can sometimes be hijacked, which makes them stream false traffic to your inventory. Open the referral traffic section and check the marker you already know: website name, number of sessions, bounce rate, session duration.
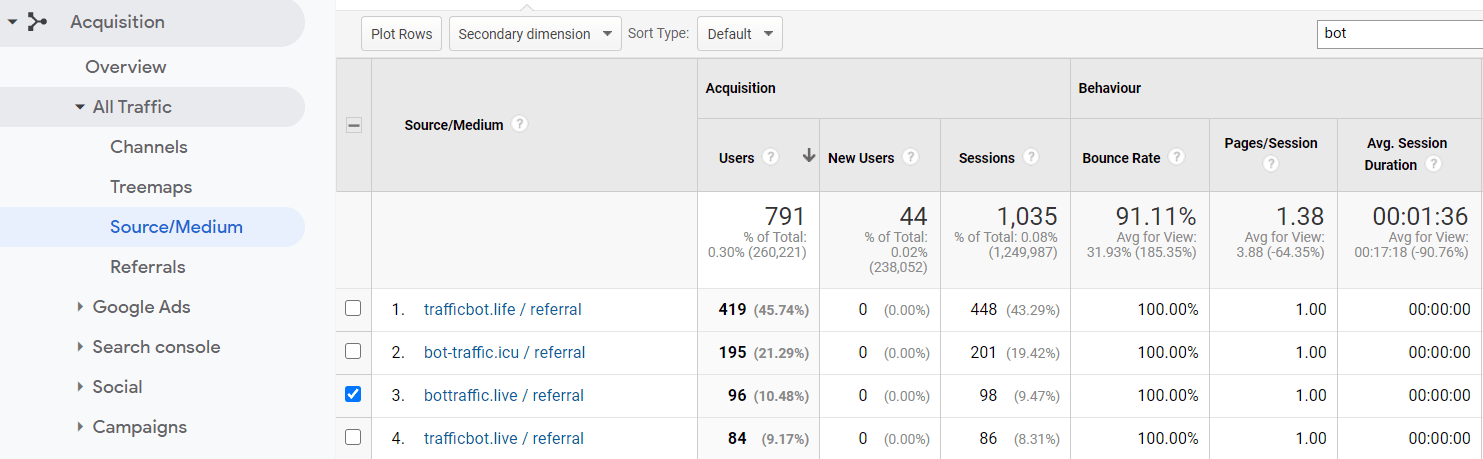
Use fake traffic detection tools
It’s also worth noting that some bots now generate traffic that mimics customer behavior. They may be difficult to detect using the above methods. Not to worry, you have bot traffic detection tools like Forensiq by Impact, BitNinja, Imperva Bot Management, Radware Bot Manager (formerly ShieldSquare) to help you.
How to stop bot traffic?
Filtering bad bot traffic and preventing bots from causing damage to your website is possible, but the solution depends on the type of traffic source causing the problem.
Once you detect bot traffic, you’ll need to stop its action immediately. Note that not all bot traffic is terrible, and blocking bots like search engine crawlers isn’t a good idea!
Bots are like viruses. They attack your website, steal data and cause damage. Thankfully, there are ways to protect yourself from malicious bot actions. Here’s how to do it:
- Legal paid traffic: Buy traffic from well-known sources. Many publishers use traffic trading to ensure high-yielding PPC/CPM campaigns by purchasing safe traffic.
- Place robots.txt on your website to prevent bad bots from crawling your pages. Publishers should also check that the crawler settings are correct to avoid problems with AdSense ads.
- Set JavaScript for bot alerts: Set JavaScript to notify you about bots. When contextual JS detects a bot or similar element entering a website, it acts as a buzzer.
- DDOS: Install a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDOS) protection or a good anti-malware extension. Publishers with a list of offensive IP addresses use DDOS protection to prevent those IP addresses from accessing their website.
- Examine the log files: As bots attempt to overrun servers, examining the server error logs helps detect and correct the website errors from bot activities.
- Use Type-Challenge Response Tests (TCRT): Add CAPTCHA to download or signup forms. Many publishers and premium websites use CAPTCHA to prevent the action of spambots.
How to identify the bot traffic within Google Analytics?
Detecting bot traffic is the first step in ensuring you take advantage of good bots (such as appearing in SERPs) while avoiding the harmful effects of bad bots on your business.
Google Analytics is an excellent place to learn how to detect bot traffic. You’ll be able to see bot traffic when you understand its concept.
Here are the key ratios to keep track of:
- Traffic and Bounce rate: When you observe a sudden increase in traffic volume and bounce rate, it indicates bad bot traffic. An increase in bounce rate also shows that robots perform their task and leave the website without exploring additional pages.
- Junk conversions: Spam of form-filling bots can cause an increase in fake conversions, such as account creation with gibberish email addresses or contact forms using fake names and phone numbers.
- Slow site load metrics: It’s also critical to keep track of this. If your site’s load times suddenly slow down and feel sluggish, it could be due to an increase in bot traffic or a DDoS attack by a bot.
- High or low session duration: The duration of a user’s session on a website should be consistent. Bots crawling the site at a prolonged rate explains the increase in session duration. Also, bots clicking through pages on the site faster than humans can unexpectedly cause a drop in session duration.
How to set up bot filters in Google analytics
Google Analytics allows you to block malicious traffic with several features. But not all of them are transparent and practical. We’re going to highlight one that works in most cases: the bot filtering feature. It cuts off all harmful traffic, allowing you to test all filters safely and saving you time for further investigations.
Here’s how to find and switch it on. Go to your Google Analytics Admin section, and find View Settings (on the View tab).
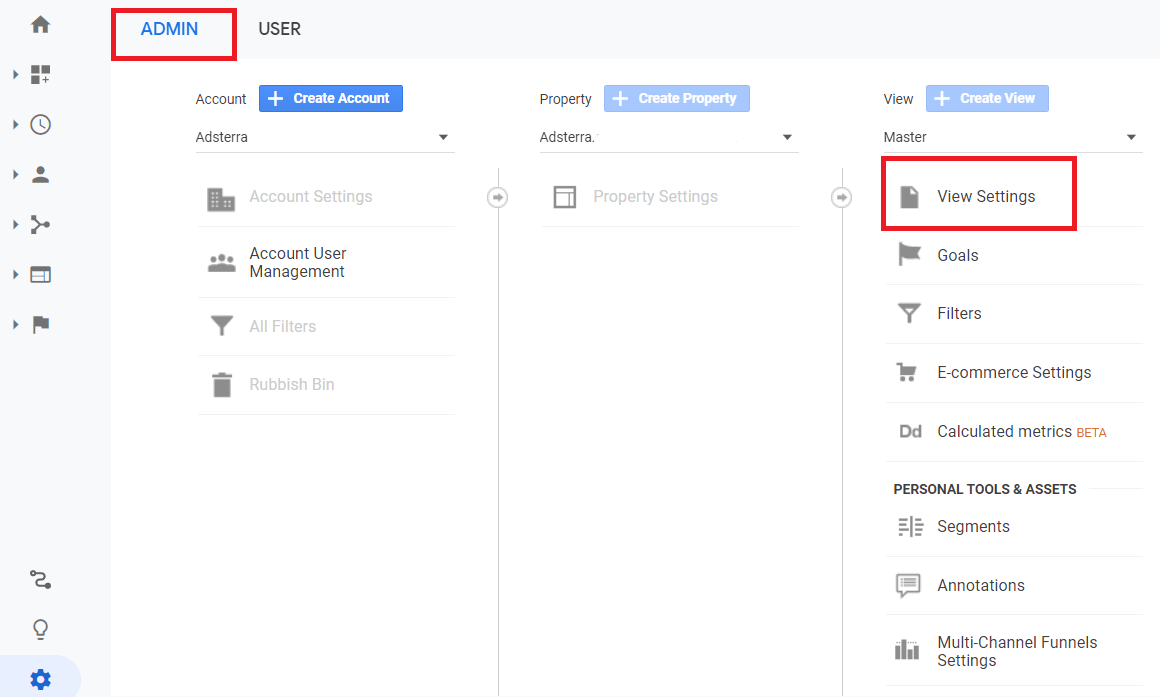
Scroll down till you see a Bot Filtering checkbox. Check the box and click Done.
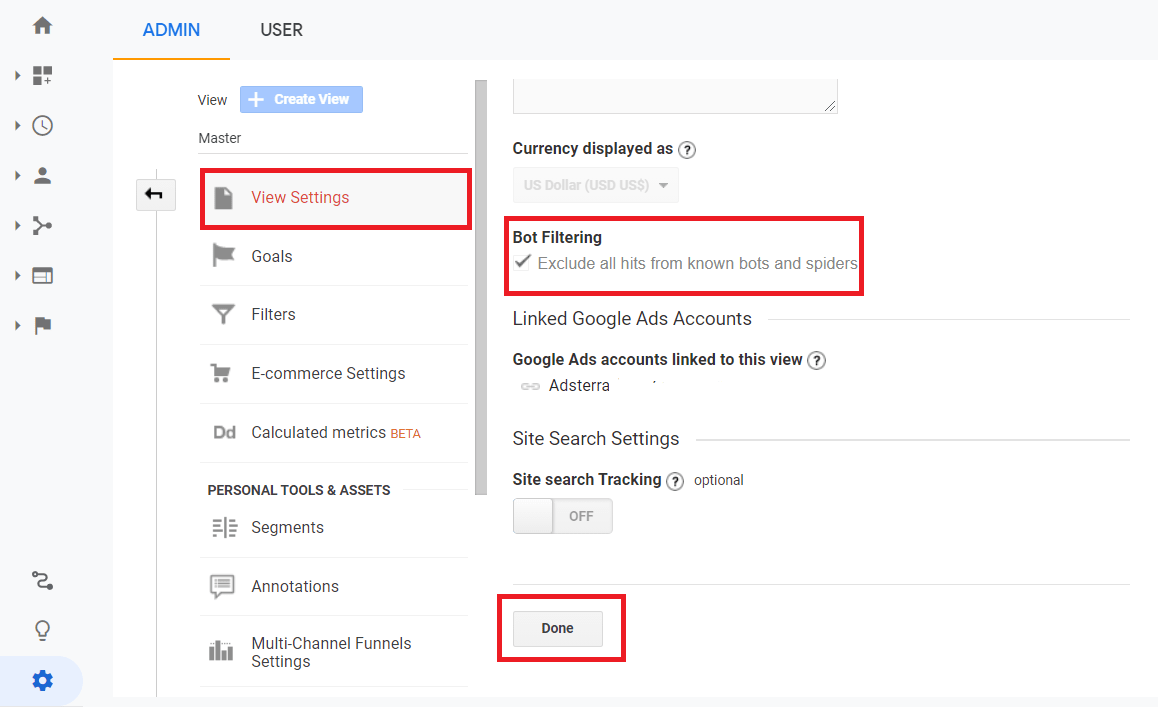
Note!
This feature has advanced to filter spam referrers, too.
Using filters to cut off bot traffic from your reports
Then try to stop all current fake traffic. These Google Analytics settings have worked well for years. They can save your statistics from attacks but not stop them.
Note!
Make sure you have an unfiltered view of your website before adding any filters. If not, create a View with no filters. You can’t track changes or compare reports otherwise. Also, clone your Main view to safely test all filters.
Creating a filter to exclude spam referrals
After creating a Test view that is a clone of your Main View, add a filter to exclude spam referrers you have previously detected.
1. Go to the Admin section, then navigate to the View you need to create a filter in.
2. Find the VIEW column and select Filters. Choose Add Filter. You need to have Edit permission to add filters.
3. Select Create new filter and enter its name.
4. Pick Custom for the Filter type.
5. Choose Exclude for Filter field and then pick Campaign source from the list.
In the Filter pattern field, you will need to enter all bot domains that you traced before. Enter them one by one using regular expressions. See all instructions by Google and check the list of regular expressions.
Example: botsource\.com|secondbotsource\.com|.*badbotsubdomain\.com
Finally, click Save.
Turn on Google Analytics alerts
While it does not block bot traffic, it does keep things in check. You can set up alerts for each Account View. You can set the frequency of alerts as well as the conditions under which Google will notify you.
Conclusion
You’ll want to take every measure possible to defend against bot attacks after learning about the dangers of bad web bots and how they can harm your business. You can take some preventative measures on your own, such as putting CAPTCHAs on forms and using a good website builder to keep your site safe from hackers and malware.
When performing analyses, you can try filtering known bots, but blocking bot traffic is nearly impossible. Install the updated security tools to counter these potentially destructive scripts and ensure your site is protected. It’s vital to select a solution that has a high level of accuracy, provides real-time detection and mitigation, and continually learns and improves
